Introduction
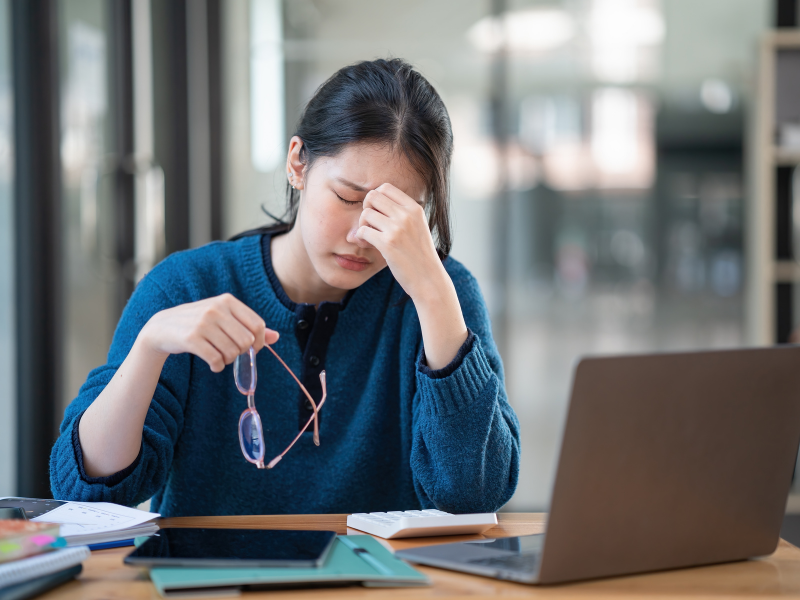
Mental health is a complex and multifaceted aspect of our well-being. It encompasses our emotional, psychological, and social well-being, affecting how we think, feel, and act. While various factors influence mental health, including environment, upbringing, and life experiences, a question that often arises is whether mental health issues are hereditary.
In this article, we explore the fascinating connection between genetics and mental health. We delve into the role of inheritance in conditions such as depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia. Whether you’re interested in understanding your own mental health or have concerns about potential hereditary factors, this article will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of this topic.
Are Mental Health Issues Hereditary?

Although the interplay of genetic and environmental factors plays a central role in mental health, researchers have been studying the hereditary aspects of mental health issues for decades. While it’s important to note that not all mental health issues have a genetic basis, studies have shown that a significant number of mental health conditions do have a hereditary component.
Let’s explore the key insights and findings related to mental health issues and genetics.
Genetics and Depression: Unraveling the Inheritance Puzzle

Depression is a widespread mental health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, loss of interest, and a lack of motivation. While the exact cause of depression is still not fully understood, researchers have identified genetic factors that contribute to its development.
The Role of Genetic Variations in Depression
Multiple studies have shown that genetic variations can increase the risk of developing depression. These variations can influence the production and regulation of neurotransmitters, such as serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, which play vital roles in mood regulation.
Researchers have identified specific genes, such as the serotonin transporter gene (SLC6A4), that are associated with an increased risk of depression. However, it’s crucial to remember that these genetic variations are just one piece of the puzzle and interact with environmental factors to impact an individual’s mental health.
Identical Twins: A Glimpse into the Genetics of Depression
Studying identical twins has provided invaluable insights into the hereditary nature of mental health conditions. Identical twins share nearly identical genetic material, making them ideal subjects for understanding the role of genetics in mental health. In numerous studies, researchers have observed a higher concordance rate (both twins sharing the same condition) for depression in identical twins compared to fraternal twins.
These findings suggest a strong genetic component in depression, but again, environmental factors also contribute significantly to an individual’s risk of developing the condition.
Anxiety: The Genetic Web of Worry and Fear

Anxiety disorders encompass a range of conditions characterized by excessive worry, fear, and unease. Individuals with anxiety disorders may experience symptoms such as panic attacks, phobias, or obsessive-compulsive behaviors. Understanding the genetic factors behind anxiety can help uncover potential risk factors and guide personalized treatment approaches.
The Genes Behind Anxiety Disorders
Similar to depression, multiple genes are believed to contribute to the development of anxiety disorders. One such gene, the COMT gene, has been studied extensively in relation to anxiety. The COMT gene affects the production of an enzyme called catechol-O-methyltransferase, which plays a role in the breakdown of neurotransmitters like dopamine.
Variations in the COMT gene have been associated with an increased risk of anxiety disorders. However, as with depression, genes are not the sole determinants of anxiety, as environmental and psychological factors also play significant roles.
Exploring the Role of Epigenetics
Epigenetics refers to changes in gene expression that do not involve alterations in the underlying DNA sequence. It is a fascinating field of research that has shed light on how environmental factors can influence gene expression.
Studies have suggested that various environmental factors, such as childhood trauma or chronic stress, can modify the activity of genes associated with anxiety disorders. These epigenetic modifications can have long-lasting effects on an individual’s mental health, potentially increasing their susceptibility to anxiety.
Bipolar Disorder: Balancing the Genetic Puzzle
Bipolar disorder is a chronic mental health condition characterized by extreme mood swings, ranging from depressive episodes to manic episodes. Understanding the genetic factors associated with bipolar disorder is crucial for early intervention and improving treatment outcomes.
The Genetic Links to Bipolar Disorder
Multiple studies have indicated a genetic component in bipolar disorder. Researchers have identified specific genes involved in neurotransmitter signaling pathways, such as the CACNA1C gene, as potential contributors to the condition. However, as with other mental health issues, the genetic landscape of bipolar disorder is complex, and multiple genes likely interact to influence an individual’s risk.
The Impact of Family and Twin Studies
Family and twin studies have played a vital role in elucidating the hereditary nature of bipolar disorder. These studies have consistently shown a higher likelihood of developing bipolar disorder for individuals who have a close family member with the condition. Additionally, identical twin studies have provided further evidence of a genetic predisposition, with a higher concordance rate for bipolar disorder in identical twins compared to fraternal twins.
Schizophrenia: Unraveling the Genetic Mysteries
Schizophrenia is a chronic mental disorder characterized by abnormal thoughts, perceptions, emotions, and behavior. While the exact cause of schizophrenia remains unknown, research has demonstrated a strong genetic component in the condition.
Complex Genetics of Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is considered a complex disorder, meaning that it likely involves the interaction of multiple genetic and environmental factors. Researchers have identified numerous genes associated with schizophrenia, including the DISC1 gene, which plays a role in neural development.
Additionally, copy number variations (CNVs), which involve deletions or duplications of genetic material, have also been implicated in schizophrenia. These CNVs can disrupt the functioning of genes involved in crucial brain development processes, potentially leading to the development of the condition.
Genetic Heritability and Schizophrenia
Family and twin studies have provided compelling evidence for the hereditary nature of schizophrenia. Individuals with a first-degree relative (such as a parent or sibling) with schizophrenia face a higher risk of developing the condition themselves. Twin studies have further illustrated the genetic influence, with higher concordance rates in identical twins compared to fraternal twins.
FAQs
FAQ 1: Can mental health issues skip a generation?
Mental health issues can appear to skip a generation due to the complex interplay of genetic and environmental factors. While it may seem like a condition has skipped a generation, it is more likely that subtle genetic variations and environmental influences have contributed to the risk of the disorder.
FAQ 2: Can someone inherit mental health issues even if their parents don’t have them?
Yes, it is possible for individuals to inherit mental health issues even if their parents don’t have them. Mental health is influenced by a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. While a family history of mental health issues increases the risk, other factors can also contribute to an individual’s vulnerability.
FAQ 3: Do all individuals with a family history of mental health issues develop the conditions themselves?
No, not all individuals with a family history of mental health issues will develop the conditions themselves. A family history indicates an increased risk, but it does not guarantee that an individual will develop mental health issues. The intricate interplay between genetics and environmental factors influences an individual’s susceptibility to these conditions.
FAQ 4: Can mental health issues be completely attributed to genetics?
No, mental health issues cannot be completely attributed to genetics alone. While genetic factors play a significant role, environmental influences, such as traumatic experiences, stress, and social factors, also contribute to the development of mental health issues.
Conclusion
Exploring the question, “Are mental health issues hereditary?” reveals a complex relationship between genetics and mental health. While genetic factors undoubtedly contribute to the development of mental health issues such as depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia, they are not the sole determinants. Environmental, psychological, and lifestyle factors also play crucial roles in an individual’s susceptibility to these conditions.
It is essential to approach mental health with a holistic perspective, considering the multifaceted nature of these issues. By understanding the interplay between genetics and environmental factors, individuals can make informed decisions about their mental health and access appropriate support and treatment options.
Remember, if you have concerns about your mental health or suspect a hereditary component, reach out to a qualified healthcare professional who can provide personalized guidance and support. Mental health is a journey, and together, we can foster a greater understanding and compassion for the challenges many individuals face.